The The Effect of Immersion on Tensile Strength of Fiberglass-Polyester Composites for Shipbuilding Materials
Keywords:
Fiberglass-Polyester , Submersion, Tensile StrengthAbstract
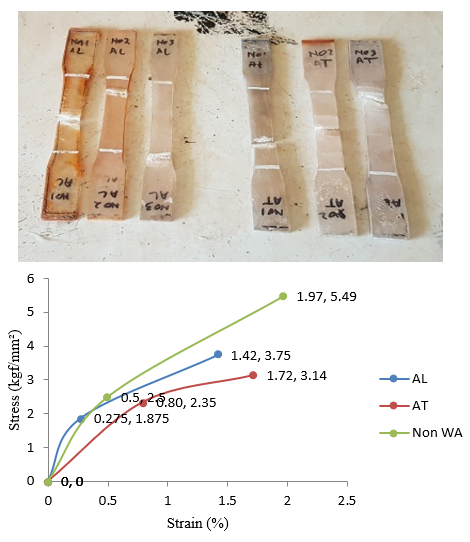
The use of fiberglass-based composites is often found in shipbuilding because it has many advantages. The advantages of fiberglass-based composites are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, easy to shape, and affordable prices. However, fiberglass also has undesirable properties, namely hygroscopicity due to its chemical constituents. Moisture absorption by these composites has several detrimental effects on their properties, and thus affects their long-term performance. For example, increased humidity reduces their mechanical properties. The purpose of this study was to determine how the difference in absorption rate between sea water and fresh water in fiberglass-polyester material and how the effect of immersion on the tensile strength of fiberglass-polyester material for shipbuilding materials. The method used in this study is an experimental method that uses a tensile testing machine by varying the differences in immersion methods on the test specimen for 30 days. The tensile testing process is carried out shortly after the specimen is removed from the water, and first weighed so that the percentage of water absorption can be found. The result of the percentage of composite water content tended to increase with the length of immersion time but the increase was 0.073% in the specimens with sea water immersion and 0.220% in the specimens with the immersion process of fresh water. Whereas in the tensile test of fiberglass-polyester material for shipbuilding materials immersed in water for 30 days, it was 3.75 kgf/mm2 in the seawater immersion process and 3.14 kgf/mm2 in the fresh water immersion specimen.
Downloads